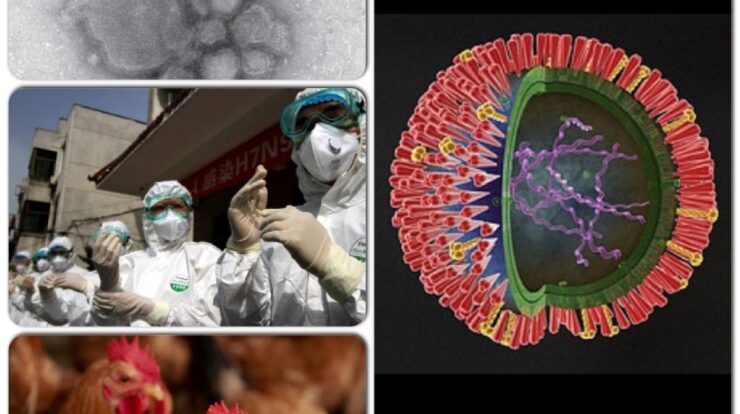
H7N9, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has emerged as a significant threat to public health. With its ability to cause severe respiratory illness in humans, understanding its characteristics, transmission, and prevention is crucial.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of H7N9, exploring its origins, evolution, symptoms, treatment options, and global impact.
H7N9 Virus Overview
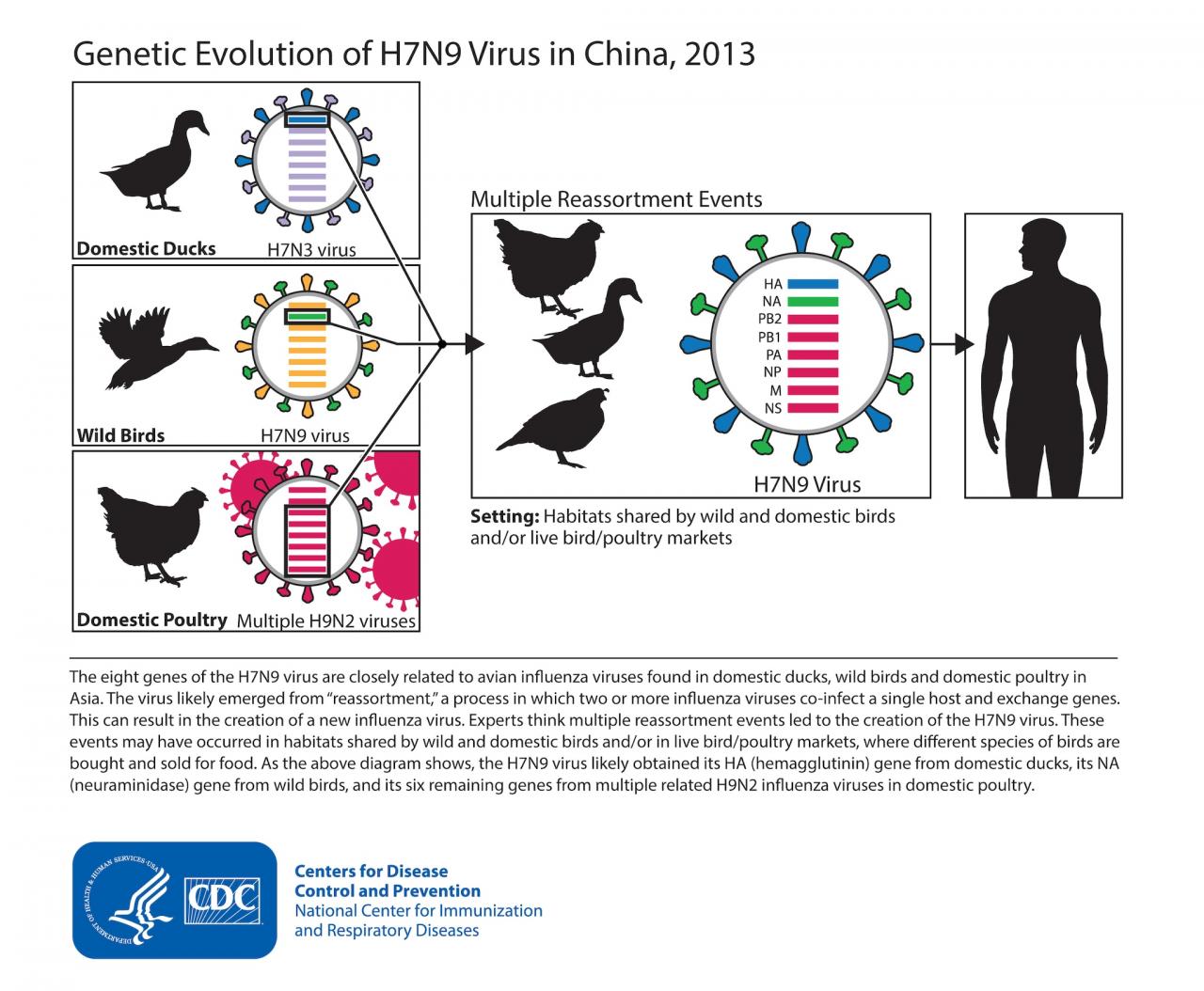
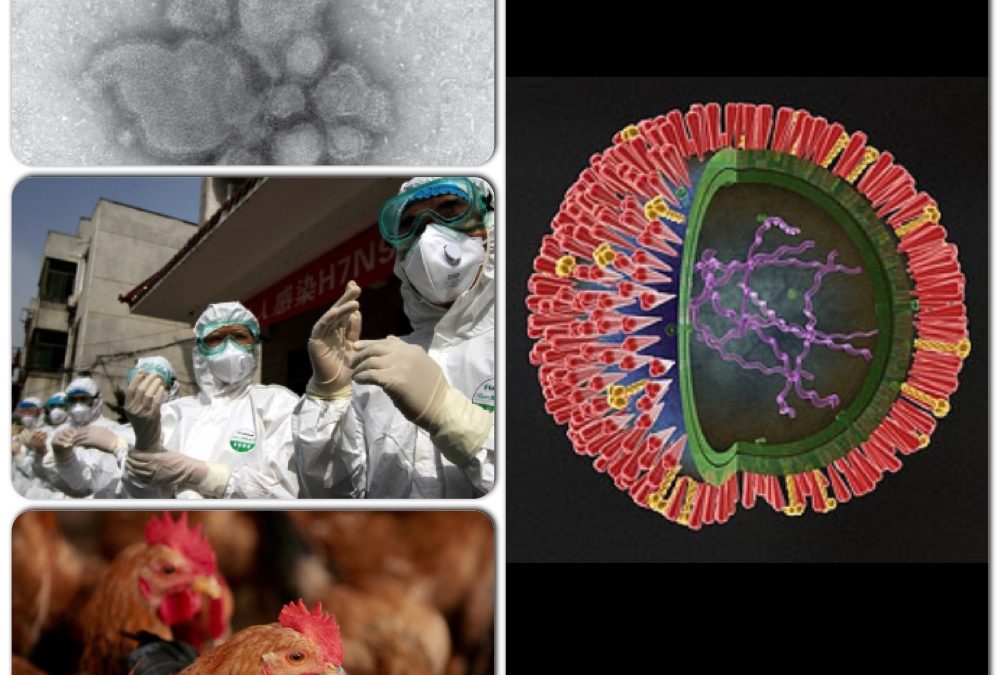
H7N9 is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that emerged in China in 2013. It is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which is responsible for causing respiratory infections in birds and humans.
The H7N9 virus is classified as an orthomyxovirus, which means it is a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA virus. The virus particle is composed of a helical nucleocapsid surrounded by a lipid envelope. The envelope contains two glycoproteins, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), which are essential for the virus’s attachment to and entry into host cells.
H7N9 viruses are primarily found in poultry, particularly chickens and ducks. The virus can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected birds or their secretions, or through exposure to contaminated environments.
H7N9 Infection
H7N9 infection in humans can cause a range of symptoms, from mild respiratory illness to severe pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The incubation period of the virus is typically 2-7 days.
Common symptoms of H7N9 infection include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. In severe cases, the virus can cause difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, and respiratory failure.
Diagnosis of H7N9 infection is confirmed by laboratory testing, such as real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or virus isolation.
H7N9 Pathogenesis and Treatment

The pathogenesis of H7N9 infection involves the virus’s attachment to and entry into host cells via the HA and NA glycoproteins. Once inside the host cell, the virus replicates and produces new viral particles, which are then released from the cell and can infect other cells.
The virus has a predilection for the lower respiratory tract, where it can cause inflammation and damage to the lung tissue. In severe cases, the infection can lead to ARDS, which is a life-threatening condition characterized by fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Treatment for H7N9 infection includes antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, which inhibit the virus’s replication. Supportive care, such as oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation, may also be necessary in severe cases.
H7N9 Prevention and Control
Preventive measures for H7N9 infection include avoiding contact with infected birds or their secretions, practicing good personal hygiene, and maintaining proper respiratory etiquette.
Vaccination is also an important preventive measure. Several vaccines have been developed to protect against H7N9 infection, and they are recommended for individuals at high risk of exposure to the virus, such as poultry workers and healthcare professionals.
Surveillance and control strategies are essential for mitigating H7N9 outbreaks. These strategies include monitoring poultry populations for the virus, implementing quarantine measures, and culling infected birds.
H7N9 Public Health Impact
H7N9 infection has had a significant public health impact, particularly in China where the majority of cases have been reported. The virus has caused widespread illness and death, and has led to economic losses due to the culling of poultry and the disruption of trade.
The global distribution of H7N9 infection is limited, but the virus has the potential to spread to other regions. Continued surveillance and preparedness measures are essential to prevent and control future outbreaks.
H7N9 Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research efforts are focused on understanding the pathogenesis of H7N9 infection, developing more effective vaccines and antiviral therapies, and improving surveillance and control strategies.
Future research directions include investigating the molecular mechanisms of viral replication and transmission, developing new diagnostic tools, and evaluating the effectiveness of different prevention and control measures.
Last Point
As research into H7N9 continues, ongoing efforts in vaccine development, antiviral therapies, and surveillance are essential to mitigate its impact on public health. Understanding the complexities of this virus empowers us to implement effective prevention and control measures, safeguarding communities worldwide.